Back to Course List
Confined Space: Confined Space Hazards

- Product ID
- cshazmpg
- Training Time ?
- 57 to 114 minutes
- Language(s)
- English
- Video Format
- Standard Definition
- Required Plugins
- MasteryNet Player
- Lesson Interactions
- 13
- Quiz Questions
- 40


Overview
Online Confined Spaces Training
In this course, your workers will learn learn about atmospheric, confinement, process, entry, and exit hazards associated with a confined space. They will learn how to control these hazards through proper isolation, purging, cleaning, ventilation, testing and monitoring. They will also learn about the permit process in this confined space training course.
![]() This course is in the Advantage™ format, to read about Advantage™ features click here.
This course is in the Advantage™ format, to read about Advantage™ features click here.

- Rich multimedia presentation with interactions and quiz
- Print certificate and wallet card
- You have 30 days to complete the course
Workplaces
Categories
Audience
For all workers who work around or near a confined space.
Topics
The course presents the following topical areas:
-
Confinement
- Entry and exit dangers
- Difficult to occupy
- Part of a process
-
Atmosphere
- Entering the space's atmosphere
- Asphyxiating atmospheres
- Toxic atmospheres
- Flammable atmospheres
-
Processes
- Energy related hazards
- Content related hazards
- Other hazards
-
Controls
- Isolation
- Purging, cleaning, and ventilation
- Testing and monitoring
- Protective equipment
- Work practices
-
Permits
- The permit program
- The permit checklist
Intended Performance Outcomes
Upon successful completion of this course you will be better prepared to:
-
Explain confinement hazards.
- Define confined space.
- List dangers posed by the shape and size of the space.
- List dangers posed by the shape and size of the entrance.
- Define process hazard.
- List hazards caused by lack of design for human occupancy.
- List injuries and accidents that can result from limited ability
-
Respect the danger of confinement hazards.
- Explain the multiplicity of risk posed by confined spaces.
- Explain how confinement hazards affect the senses.
-
Explain atmospheric hazards.
- List the three categories of atmospheric hazards.
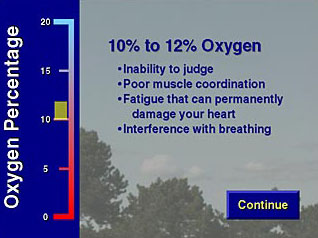
- Define an oxygen deficient atmosphere.
- Describe conditions that can cause oxygen deficiency.
- Compare the behavior of heavy and light gases.
- Describe conditions that can lead to fire and explosion.
- Describe conditions that can cause toxic atmospheres.
-
Respect the danger of atmospheric hazards.
- Explain the significance of breaking the plane.
- Explain the danger of oxygen deficiency.
- Explain how some toxins can affect the sense of smell.
- Explain why rescuers are often victims.
- List ways toxic atmospheres effect the respiratory system and body.
-
Respect energy and other process hazards.
- Recognize the dangers posed by radiant heat.
- Explain the effects of excessive noise and vibration on the body.
- List conditions and actions outside the space that create hazards inside the space.
- Explain the dangers posed by the system in a process space.
-
Explain the dangers of content hazards.
- List ways toxic substances can harm the body.
- Explain the dangers posed by biological hazards.
- Describe types of hazardous conditions posed by substances contained in confined spaces.
- Explain the dangers of finely-divided solids.
-
Value space preparation prior to entry.
- List hazards that isolation controls.
- List hazards that purging and cleaning control.
- List hazards that ventilation controls.
- List hazards that atmospheric testing and monitoring controls.
- Relate control measures to personal safety.
-
Value hazard control during entry.
- Relate work practices to personal safety.
- Demonstrate a commitment to proper control measures.
- List common types of personal protective equipment.
-
Select proper control measures.
- Explain how to control mechanical hazards.
- Explain how to control atomospheric hazards.
- Explain how to control process hazards.
-
Value the permit program.
- Explain the basic concepts of the permit program.
- Recognize the permit program as a systematic approach to controlling hazards.
- Acknowledge personal responsibility in following permit procedures.
- Relate personal safety to adherence to permit procedure.
- Demonstrate a commitment to the permit system.
© Mastery Technologies, Inc.

